Region:Asia
Author(s):Geetanshi
Product Code:KRAA4520
Pages:92
Published On:September 2025
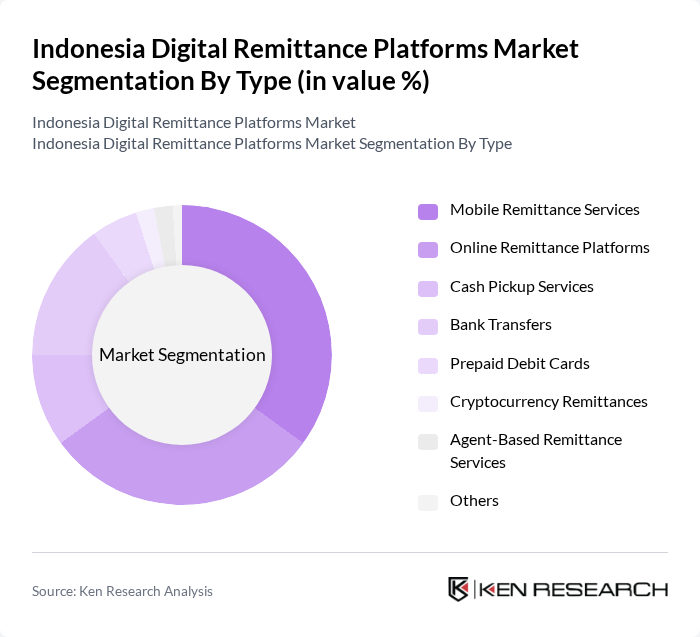
By Type:The digital remittance platforms in Indonesia can be categorized into several types, including Mobile Remittance Services, Online Remittance Platforms, Cash Pickup Services, Bank Transfers, Prepaid Debit Cards, Cryptocurrency Remittances, Agent-Based Remittance Services, and Others. Mobile Remittance Services and Online Remittance Platforms are particularly popular, driven by widespread smartphone adoption, expanding internet access, and the growing preference for seamless, real-time transactions. The increasing use of digital wallets and mobile apps further accelerates the shift toward these channels .
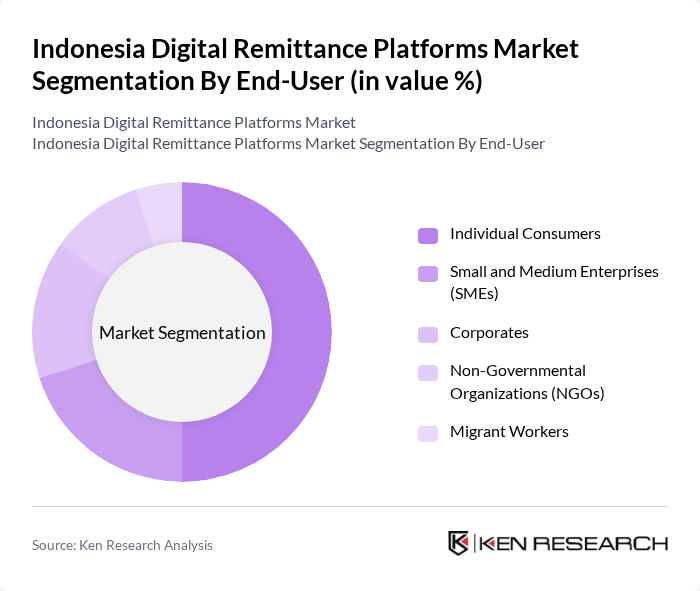
By End-User:The end-users of digital remittance platforms in Indonesia include Individual Consumers, Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs), Corporates, Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs), and Migrant Workers. Migrant Workers and Individual Consumers are the primary users, frequently sending money to support families and personal needs. The adoption of digital remittance services by SMEs is also rising, reflecting the increasing globalization of business and the need for efficient cross-border payment solutions. The growing accessibility of digital platforms is expanding participation among small businesses and NGOs .
The Indonesia Digital Remittance Platforms Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as Gojek, DANA, OVO, Wise (formerly TransferWise), Western Union, PayPal, Xendit, Bank Negara Indonesia (BNI), CIMB Niaga, Bank Mandiri, Bank Central Asia (BCA), Jenius (by Bank BTPN), LinkAja, RemitPro, and Indomaret contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space .
The future of Indonesia's digital remittance market appears promising, driven by technological advancements and evolving consumer preferences. As mobile wallet adoption continues to rise, with over30 million usersprojected in future, service providers will likely enhance their offerings to meet customer demands. Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence for customer service and the focus on sustainable practices will shape the competitive landscape, fostering innovation and improving user experiences in the remittance sector.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Type | Mobile Remittance Services Online Remittance Platforms Cash Pickup Services Bank Transfers Prepaid Debit Cards Cryptocurrency Remittances Agent-Based Remittance Services Others |
| By End-User | Individual Consumers Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) Corporates Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs) Migrant Workers |
| By Payment Method | Bank Transfers Mobile Wallets Cash Payments Credit/Debit Cards QR Code Payments |
| By Transaction Size | Micro Transactions (Below USD 100) Small Transactions (USD 100–500) Medium Transactions (USD 500–2,000) Large Transactions (Above USD 2,000) |
| By Frequency of Use | One-time Users Regular Users (Monthly/Weekly) High-Frequency Users (Daily) |
| By Geographic Reach | Domestic Remittances International Remittances (Inbound) International Remittances (Outbound) |
| By Customer Segment | Expatriates Students Migrant Workers Unbanked/Underbanked Population Others |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Expatriate User Insights | 100 | Migrant Workers, International Students |
| Local User Preferences | 80 | Young Professionals, Small Business Owners |
| Service Provider Feedback | 60 | Product Managers, Marketing Directors |
| Regulatory Impact Assessment | 40 | Policy Makers, Financial Regulators |
| Technological Adoption Trends | 50 | IT Managers, Fintech Innovators |
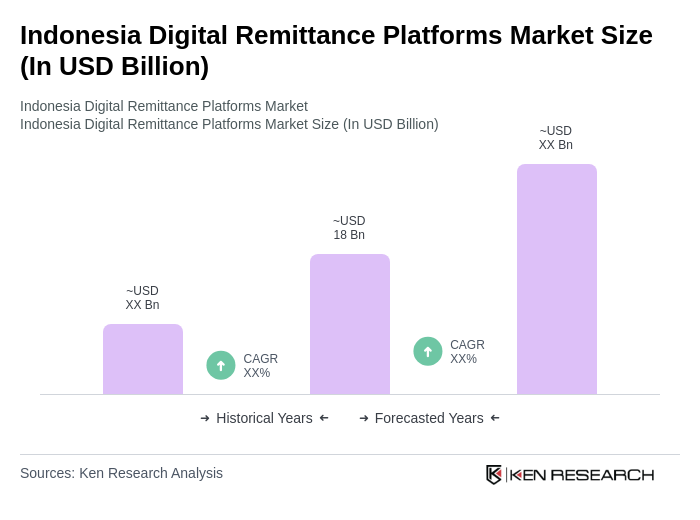
The Indonesia Digital Remittance Platforms Market is valued at approximately USD 18 billion, reflecting significant growth driven by the increasing number of Indonesian migrant workers, the adoption of digital financial services, and enhanced mobile and internet connectivity.