Region:Asia
Author(s):Geetanshi
Product Code:KRAA4163
Pages:88
Published On:January 2026
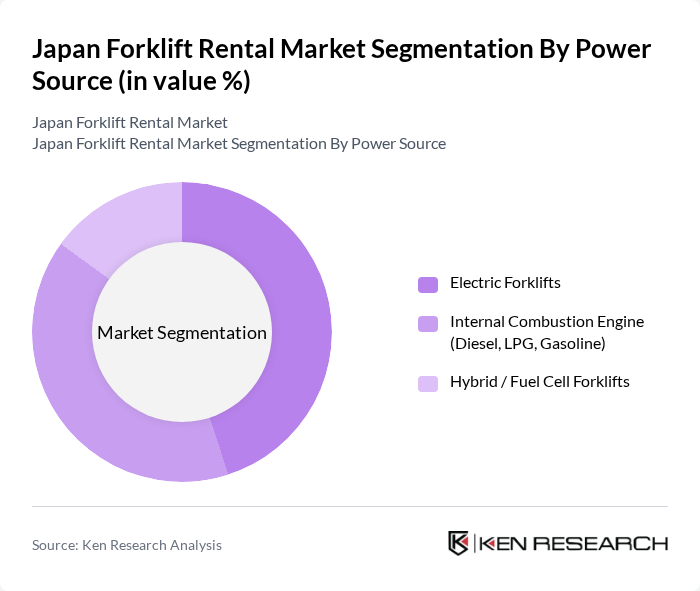
By Power Source:The market is segmented into three primary power sources: Electric Forklifts, Internal Combustion Engine (Diesel, LPG, Gasoline), and Hybrid / Fuel Cell Forklifts. Electric Forklifts are gaining traction due to their eco-friendliness, compliance with tightening emission norms, and lower operating and maintenance costs, and electric models already account for the majority of the broader Japan forklift market revenue. Internal Combustion Engine models remain popular for heavy-duty, outdoor, and long-shift applications where refueling speed is critical, particularly in construction and heavy manufacturing. Hybrid and Fuel Cell Forklifts are emerging as innovative solutions, supported by OEM pilots and government interest in hydrogen and alternative fuels, appealing to businesses looking for versatile low?emission options in high-utilization environments.
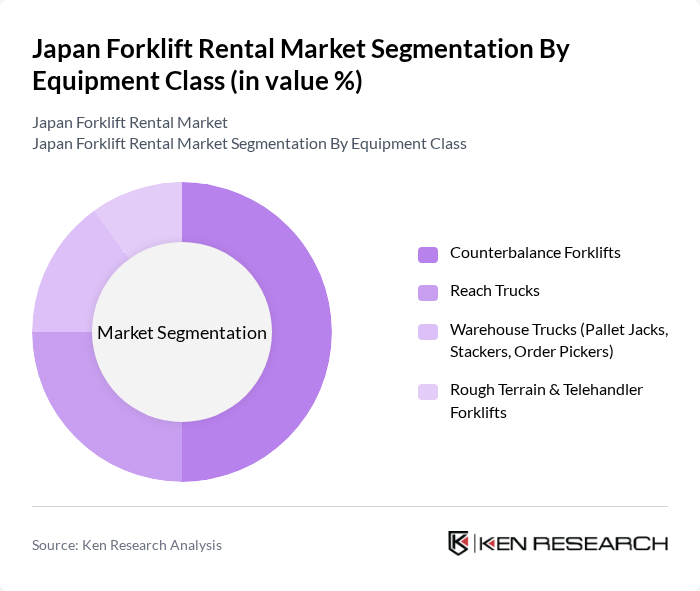
By Equipment Class:The equipment class segmentation includes Counterbalance Forklifts, Reach Trucks, Warehouse Trucks (Pallet Jacks, Stackers, Order Pickers), and Rough Terrain & Telehandler Forklifts. Counterbalance Forklifts dominate the market due to their versatility, wide capacity range, and use across factories, logistics centers, and general warehousing. Reach Trucks are preferred in high?bay warehouses and distribution centers for their ability to operate in narrow aisles and maximize storage density, particularly in e?commerce and 3PL facilities. Warehouse Trucks (such as pallet jacks, stackers, and order pickers) are essential for efficient intra?warehouse movements and order fulfillment, while Rough Terrain & Telehandler Forklifts cater to construction, infrastructure, and outdoor industrial applications where uneven surfaces and extended reach are required.
The Japan Forklift Rental Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as Toyota Industries Corporation, Mitsubishi Logisnext Co., Ltd., Komatsu Ltd., Nippon Yusoki Co., Ltd. (Nichiyu), TCM Corporation, UniCarriers Corporation, Nishio Rent All Co., Ltd., Kato Lift Co., Ltd., KION Group AG (Linde, STILL), Jungheinrich AG, Crown Equipment Corporation, Hyster-Yale Materials Handling, Inc., Doosan Industrial Vehicle, Clark Material Handling Company, Manitou Group contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, telematics-enabled fleet management, and value-added service delivery such as full-service and long-term rental contracts.
The Japan forklift rental market is poised for significant evolution, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer preferences. As automation becomes more prevalent in material handling, companies will increasingly favor rental models that provide access to the latest equipment without the burden of ownership. Additionally, the push for sustainability will likely accelerate the adoption of electric forklifts, aligning with government incentives and environmental regulations. This dynamic landscape presents opportunities for growth and innovation in the rental sector.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Power Source | Electric Forklifts Internal Combustion Engine (Diesel, LPG, Gasoline) Hybrid / Fuel Cell Forklifts |
| By Equipment Class | Counterbalance Forklifts Reach Trucks Warehouse Trucks (Pallet Jacks, Stackers, Order Pickers) Rough Terrain & Telehandler Forklifts |
| By End-Use Industry | Warehousing & Logistics / 3PL Manufacturing (Automotive, Electronics, Machinery, Others) Construction & Civil Engineering Retail & Wholesale (Including E-commerce Fulfilment) Ports, Airports & Rail Yards Others (Utilities, Government, Agriculture) |
| By Load Capacity | Up to 3 Tons to 5 Tons Above 5 Tons |
| By Rental Duration | Short-term / Spot Rentals (< 1 Month) Medium-term Rentals (1–12 Months) Long-term / Contract Rentals (> 12 Months) |
| By Region | Kanto Kansai Chubu Hokkaido & Tohoku Chugoku & Shikoku Kyushu & Okinawa |
| By Customer Type | Small and Medium Enterprises Large Corporations Government & Public Sector Entities Rental / Leasing Intermediaries |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Sector Forklift Usage | 140 | Operations Managers, Production Supervisors |
| Construction Equipment Rental Insights | 100 | Project Managers, Equipment Rental Coordinators |
| Warehouse Management Practices | 110 | Warehouse Managers, Logistics Coordinators |
| Retail Sector Forklift Demand | 70 | Supply Chain Managers, Inventory Control Specialists |
| Technological Adoption in Forklift Operations | 80 | IT Managers, Automation Specialists |
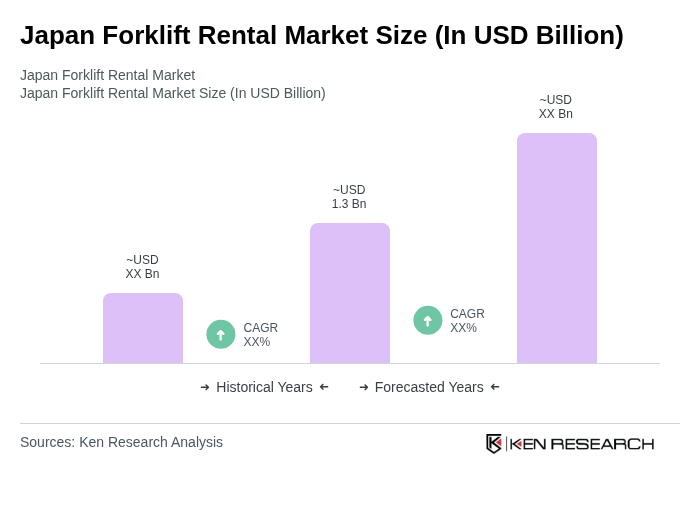
The Japan Forklift Rental Market is valued at approximately USD 1.3 billion, reflecting its significant role within the Asia Pacific forklift rental market and its contributions to the national forklift and construction equipment rental industries.