Region:Asia
Author(s):Shubham
Product Code:KRAA6454
Pages:86
Published On:January 2026
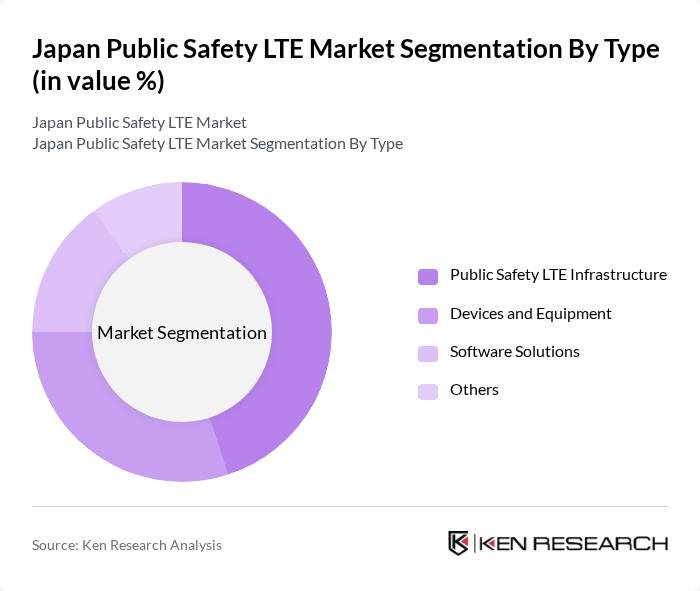
By Type:The market is segmented into Public Safety LTE Infrastructure, Devices and Equipment, Software Solutions, and Others. Among these, Public Safety LTE Infrastructure is the leading sub-segment, driven by the increasing investments in network upgrades and expansions to support emergency services. The demand for reliable and high-speed communication systems has led to significant advancements in infrastructure, making it a priority for government agencies and public safety organizations.
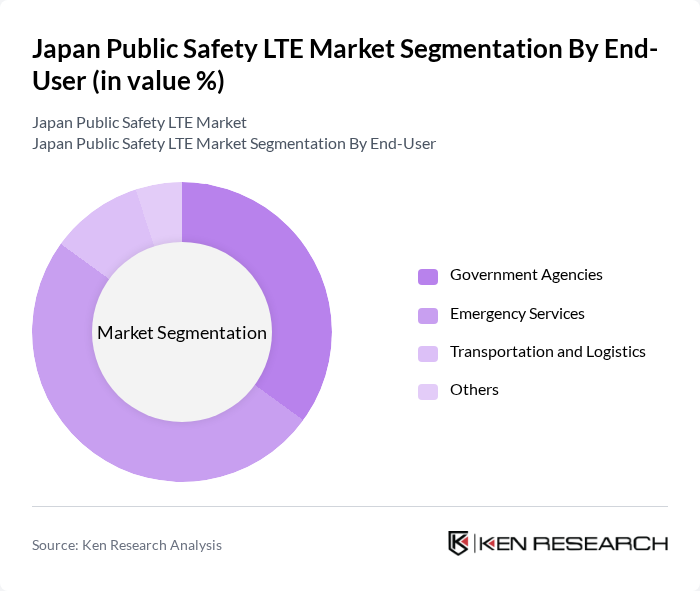
By End-User:The end-user segmentation includes Government Agencies, Emergency Services, Transportation and Logistics, and Others. Emergency Services is the dominant sub-segment, as these organizations require immediate and reliable communication solutions to respond effectively to crises. The increasing frequency of natural disasters and public safety threats has heightened the need for advanced communication systems, making emergency services a critical focus for public safety LTE investments.
The Japan Public Safety LTE Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as NTT DOCOMO, SoftBank Corp., KDDI Corporation, Motorola Solutions, Cisco Systems, Nokia Corporation, Ericsson, Huawei Technologies, NEC Corporation, Fujitsu Limited, Samsung Electronics, ZTE Corporation, Thales Group, Bell Canada, and AT&T Inc. contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The future of the Japan Public Safety LTE market appears promising, driven by ongoing technological advancements and government support. As smart city initiatives gain momentum, the integration of LTE networks with urban infrastructure will enhance emergency response capabilities. Additionally, the collaboration between public and private sectors is expected to foster innovation, leading to the development of advanced analytics tools that improve situational awareness during emergencies, ultimately enhancing public safety outcomes.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Type | Public Safety LTE Infrastructure Devices and Equipment Software Solutions Others |
| By End-User | Government Agencies Emergency Services Transportation and Logistics Others |
| By Application | Disaster Management Law Enforcement Fire Services Others |
| By Technology | LTE Advanced G Integration Network Slicing Others |
| By Deployment Model | On-Premises Cloud-Based Hybrid Others |
| By Region | Kanto Kansai Chubu Others |
| By Investment Source | Government Funding Private Investments Public-Private Partnerships Others |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Public Safety Agencies | 100 | Emergency Response Coordinators, Fire Chiefs |
| Telecommunications Providers | 80 | Network Engineers, Business Development Managers |
| Government Regulatory Bodies | 60 | Policy Makers, Telecommunications Regulators |
| First Responder Organizations | 70 | Police Officers, Paramedics |
| Academic Institutions | 50 | Researchers, Professors in Telecommunications |
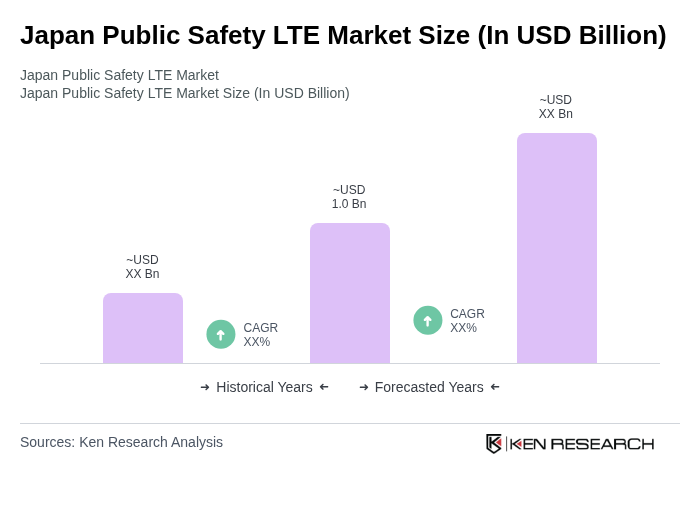
The Japan Public Safety LTE Market is valued at approximately USD 1.0 billion, driven by the increasing demand for reliable communication systems among emergency services and public safety organizations, particularly in response to natural disasters and public safety incidents.