Region:Global
Author(s):Shubham
Product Code:KRAD2610
Pages:84
Published On:January 2026
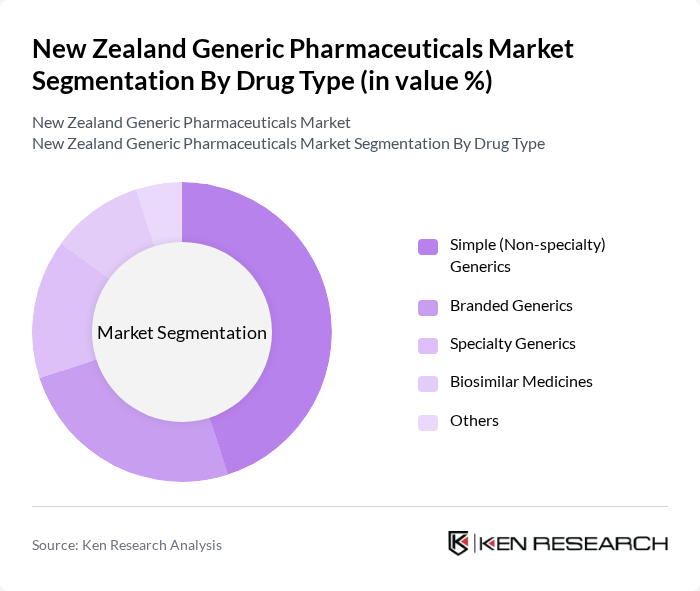
By Drug Type:The market is segmented into various drug types, including Simple (Non-specialty) Generics, Branded Generics, Specialty Generics, Biosimilar Medicines, and Others. Among these, Simple (Non-specialty) Generics dominate the market due to their widespread use for high-volume chronic and acute conditions and strong acceptance among prescribers and pharmacists in PHARMAC-funded categories. The affordability and accessibility of these generics, especially in primary care and community pharmacy settings, make them the preferred choice in a cost-sensitive healthcare environment with tight public budget controls. Branded Generics also hold a significant share, appealing to consumers and prescribers who prefer familiar brand names, particularly in over-the-counter and pharmacy-led brands, while still benefiting from lower costs compared to original patented drugs.
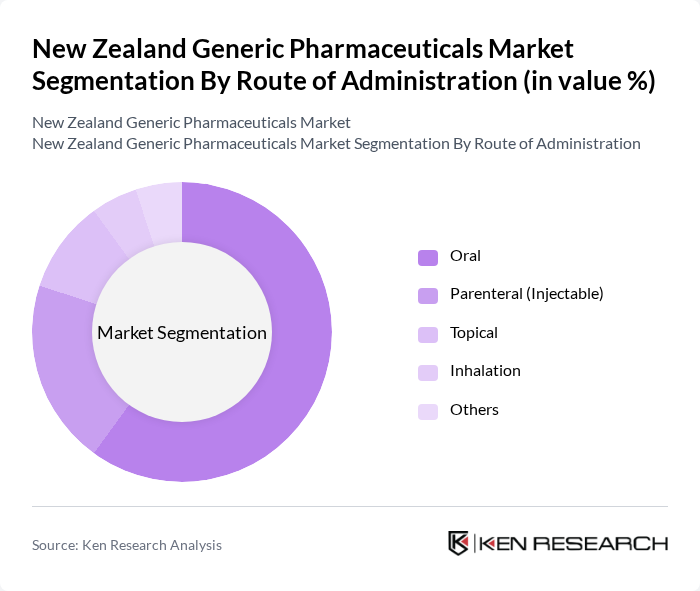
By Route of Administration:The market is segmented by route of administration into Oral, Parenteral (Injectable), Topical, Inhalation, and Others. Oral administration is the most prevalent route, accounting for a significant portion of the market due to its convenience, high patient adherence, and dominance of solid-dose generics on the PHARMAC schedule. Parenteral (Injectable) medications are also important, particularly for hospital and specialty care, including oncology, anti-infectives, and biologic or biosimilar products. The growing trend towards self-administration of injectables for chronic conditions, such as diabetes and autoimmune diseases, supported by patient education and device innovation, is expected to further support this segment.
The New Zealand Generic Pharmaceuticals Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as PHARMAC (Pharmaceutical Management Agency – Buyer / Payer Context), AFT Pharmaceuticals, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Viatris Inc. (Including Legacy Mylan Portfolio), Sandoz Group AG, Apotex Inc., Accord Healthcare, Mylan New Zealand (Historical Presence Overview), Pfizer (Including Upjohn / Off-patent Portfolio), Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories, Cipla Ltd., Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Aurobindo Pharma Ltd., Viatris / Mylan–Legacy Portfolio Competitors (Other Key Generics), Selected Local Distributors & Parallel Importers (e.g., Pharmacybrands / Green Cross Health, Others) contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The future of the New Zealand generic pharmaceuticals market appears promising, driven by ongoing government support and an increasing focus on healthcare affordability. As the population ages and healthcare expenditures rise, the demand for generics is expected to grow. Additionally, advancements in digital health solutions and personalized medicine are likely to reshape the market landscape, providing opportunities for innovation and improved patient outcomes. Companies that adapt to these trends will be well-positioned for success.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Drug Type | Simple (Non-specialty) Generics Branded Generics Specialty Generics Biosimilar Medicines Others |
| By Route of Administration | Oral Parenteral (Injectable) Topical Inhalation Others |
| By Therapeutic Area | Cardiovascular Diseases Oncology Central Nervous System Disorders Infectious Diseases Diabetes and Metabolic Disorders Respiratory Diseases Others |
| By Distribution Channel | Hospital Pharmacies Retail Community Pharmacies Online Pharmacies / E-commerce Wholesalers & Distributors Others |
| By End-User | Public Hospitals (DHB / Te Whatu Ora Network) Private Hospitals Primary Care Clinics & GP Practices Aged Care & Long-Term Care Facilities Others |
| By Manufacturer Type | Multinational Generic Manufacturers Local / Regional Manufacturers Contract Manufacturing Organizations (CMOs) Others |
| By Funding Status | PHARMAC-Funded Generics Non-funded / Private-Pay Generics |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Pharmacy Sector Insights | 120 | Pharmacy Owners, Pharmacists |
| Healthcare Provider Perspectives | 90 | General Practitioners, Specialists |
| Patient Experience with Generics | 80 | Patients using generic medications |
| Manufacturer Insights | 70 | Product Managers, Sales Directors |
| Regulatory Compliance Feedback | 60 | Regulatory Affairs Specialists, Compliance Officers |
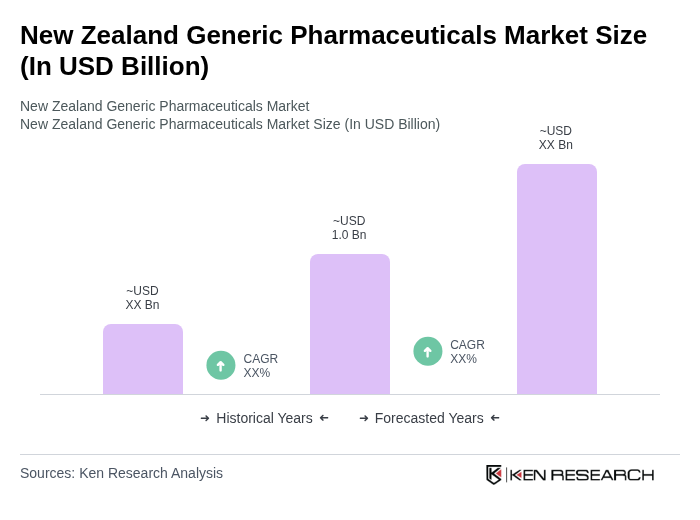
The New Zealand Generic Pharmaceuticals Market is valued at approximately USD 1.0 billion, driven by the increasing demand for cost-effective medication alternatives and the prevalence of chronic diseases in an aging population.