Region:Asia
Author(s):Dev
Product Code:KRAA3562
Pages:88
Published On:September 2025
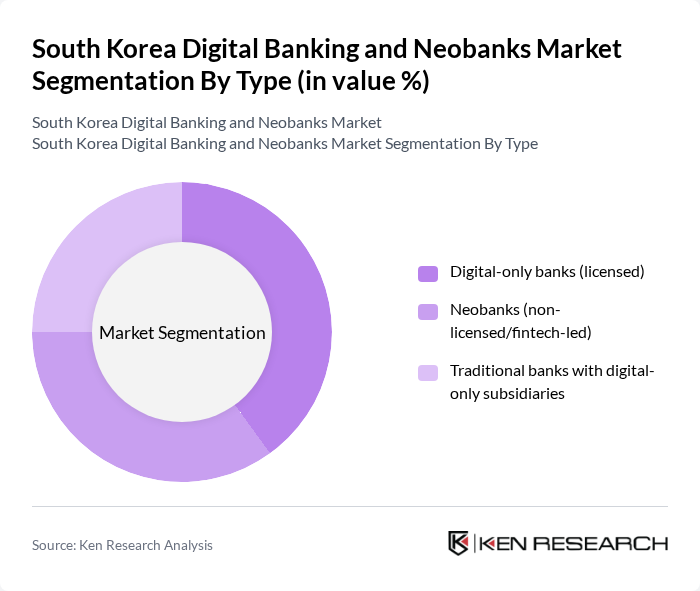
By Type:The market is segmented into three main types: Digital-only banks (licensed), Neobanks (non-licensed/fintech-led), and Traditional banks with digital-only subsidiaries. Digital-only banks such as KakaoBank, K Bank, and Toss Bank are gaining traction due to their streamlined onboarding, lower fees, and user-centric mobile experiences. Neobanks, typically fintech-led and operating without full banking licenses, appeal to younger consumers seeking innovative, mobile-first financial solutions. Traditional banks are responding to market shifts by launching digital-only subsidiaries to retain and attract digitally native customers .
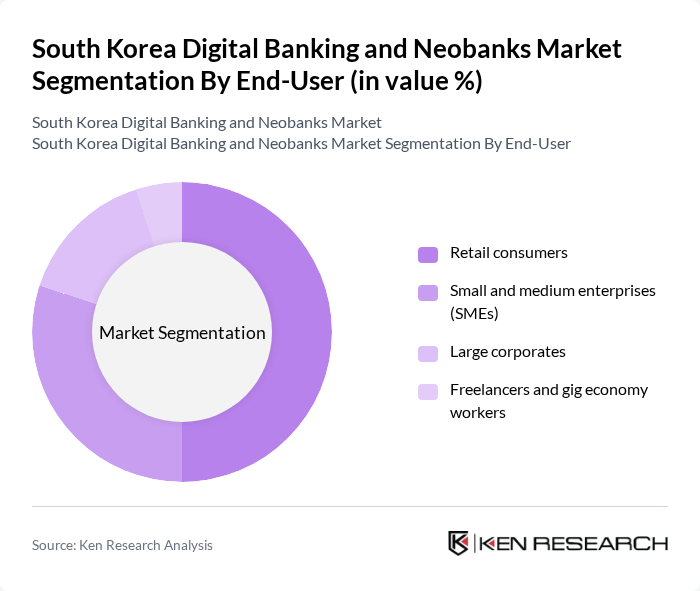
By End-User:The end-user segmentation includes Retail consumers, Small and medium enterprises (SMEs), Large corporates, and Freelancers and gig economy workers. Retail consumers account for the largest share, driven by the widespread adoption of mobile banking and digital payment solutions. SMEs are increasingly utilizing digital banking platforms for efficient payment processing, financing, and business management. Large corporates leverage digital banking for integrated treasury and cash management, while freelancers and gig economy workers benefit from flexible, app-based financial products tailored to their unique needs .
The South Korea Digital Banking and Neobanks Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as KakaoBank, Toss Bank, K Bank, KB Kookmin Bank, Shinhan Bank, Woori Bank, Hana Bank, Citibank Korea, Standard Chartered Bank Korea, Industrial Bank of Korea (IBK), DGB Daegu Bank, BNK Busan Bank, NH NongHyup Bank, Korea Development Bank (KDB), Jeonbuk Bank contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The South Korean digital banking landscape is poised for transformative growth, driven by technological advancements and evolving consumer preferences. As neobanks continue to innovate, integrating AI and machine learning for personalized services, they will likely attract a broader customer base. Additionally, the shift towards open banking will facilitate collaboration between fintechs and traditional banks, enhancing service offerings. This dynamic environment presents opportunities for neobanks to solidify their market presence and redefine customer engagement strategies in the coming years.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Type | Digital-only banks (licensed) Neobanks (non-licensed/fintech-led) Traditional banks with digital-only subsidiaries |
| By End-User | Retail consumers Small and medium enterprises (SMEs) Large corporates Freelancers and gig economy workers |
| By Service Offered | Digital payments & transfers Savings and deposit accounts Lending (personal, SME, microloans) Investment and wealth management Insurance (bancassurance, microinsurance) |
| By Customer Segment | Millennials Gen Z Seniors (Silver Generation) High-net-worth individuals |
| By Distribution Channel | Mobile apps Web platforms API/open banking integrations Third-party fintech partnerships |
| By Pricing Model | Subscription-based Transaction-based Freemium models Commission-based |
| By Geographic Presence | Metropolitan/urban areas Provincial/rural areas Cross-border/international services |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Consumer Digital Banking Usage | 120 | Retail Banking Customers, Digital Banking Users |
| Neobank Adoption Trends | 90 | Millennials, Gen Z Users, Tech-Savvy Consumers |
| Regulatory Impact on Digital Banking | 60 | Regulatory Officials, Compliance Officers |
| Fintech Innovation Insights | 50 | Fintech Entrepreneurs, Industry Analysts |
| Traditional Banks' Digital Transformation | 70 | Bank Executives, Digital Strategy Managers |
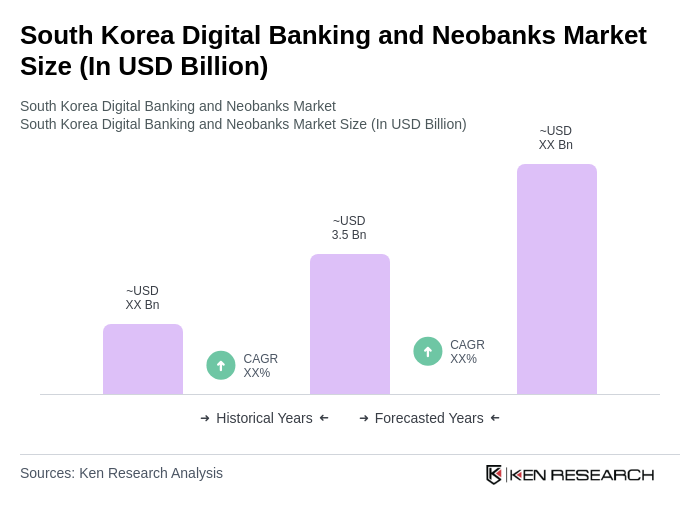
The South Korea Digital Banking and Neobanks Market is valued at approximately USD 3.5 billion, reflecting significant growth driven by mobile banking adoption, digital wallets, and real-time payment systems, supported by a tech-savvy population and government investment in fintech innovation.